If you want the Internet of Things to grow as expected, you need to connect more devices to the Internet, and Bluetooth Smart devices can do it. Bluetooth Smart devices can send data to cloud services, but of course they must also be implemented by loading a full operating system and supporting a drive that runs the software stack. But for developers, if you want to truly reflect the benefits of the Internet of Things and create a continuous connection experience, you need devices that can connect directly to the Internet.
In December 2014, the Bluetooth Technology Alliance officially launched a new Bluetooth core specification, Bluetooth 4.2. The new release brings a number of updates to developers, including lower power consumption, faster data transfer, improved security measures, and new mechanisms to improve user privacy.
For IoT device developers, the most important feature of Bluetooth 4.2 is the Internet connection. It's worth noting that it can be implemented in a variety of ways, such as IPSP, HPS, and RESTful APIs, which are important mechanisms for interconnecting the cloud and Bluetooth Smart devices.
The newly created network protocol support profile IPSP (which defines the official version of Bluetooth wireless communication between devices) enables Bluetooth to implement IPv6 connectivity, which means that Bluetooth Smart-based IoT devices are no longer connected to the cloud or only rely on smartphones or Tablet connectivity is required. It is estimated that by 2020, there will be about 28 billion devices connected to the Internet, including vehicles, doors and windows, earth drivers and ovens. With Bluetooth 4.2, these devices can access the Internet via Bluetooth via a router, an access point that supports 6LoWPAN or Bluetooth low energy technology.
The HTTP Proxy Service HPS allows Bluetooth Smart devices to communicate remotely with web servers on the public network. For example, a Bluetooth Smart temperature sensor installed in the home can send temperature readings to a cloud-based home energy efficiency recommendation service. Its implementation needs to support HPS's Bluetooth gateway, such as smart phones, personal computers, laptops, tablets and so on. It's a simple and fairly general protocol, but not all applications work with HTTP. Message-oriented applications, such as vehicle telemetry, may be more suitable for the MQTT protocol.
The RESTful API is also introduced with Bluetooth 4.2, which allows the discovery, access and control of Bluetooth Smart devices over HTTP or HTTPS. For example, by installing a Bluetooth Smart sensor for your home's windows and doors, you can monitor the real-time status of doors and windows from anywhere. Like HPS, RESTful APIs require Bluetooth gateway support. In addition, the use of HTTPS enables Bluetooth low-power technology on the opposite side of the gateway to be securely connected.
One of the key points about the RESTful API is that for devices such as broadband routers or smart TVs, all Bluetooth Smart devices within the communication range can be securely discovered and accessed from outside the home, not limited to Bluetooth 4.2 devices, but any Bluetooth-enabled device. Devices in 4.0 and later versions. This feature is significant for the Internet of Things because it means that a router with Bluetooth 4.2 controls the entire home (provided that other devices also use Bluetooth Smart). Less investment can make endless possibilities.
The difference in IPSP is that it provides device manufacturers with a way to support non-HTTP protocols in their products. IPSP will support the exchange of low-power IPv6 packets between devices via Bluetooth low-power technology. The actual packet transmission will be specified by the IETF RFC and is expected to be confirmed later this year. It also needs to support 6LoWPAN routers via Bluetooth.
Considering that the development of the Internet of Things industry is expected to drive the growth of sensors and connected devices, IPv6 is an ideal protocol for providing more IP address space. In addition, IPv6 provides tools for sensor network applications and nodes with limited processing or no mature operating systems.
Icon 1 describes IPv6 including IPSP based on the Bluetooth low energy protocol stack. UDP and TCP are examples of transport protocols, but the protocol stack can be used for any other upper layer protocol that can run on top of IPv6. The 6LoWPAN layer runs on the Bluetooth low-power L2CAP layer (which is responsible for segmentation and reassembly of packets larger than the base RF processing capability). IPv6 relies on the L2CAP dedicated channel feature, meaning that it requires Bluetooth 4.1 or newer to run.
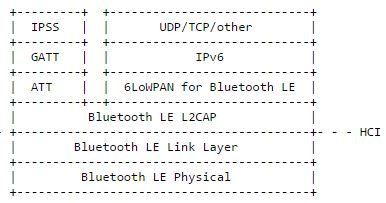
Figure 1 – IPv6 based on the Bluetooth LE protocol stack
IPv6 is suitable for remote industrial and commercial deployments, enabling remote management of each endpoint through IPv6. End-to-end IPv6 connectivity can drive the asset tracking and management industry. For example, it supports remote management of heat pump control valves in industrial buildings through cloud platforms.
The added bonus of such services goes beyond the direct benefits that IPv6 connectivity brings to developers. The ability to access and control data gives service providers a disruptive opportunity to use this data to bring more innovative cloud services to consumers and businesses, and to experience the benefits of the Internet of Things. More advantages.
With HPS, IPSP and RESTful APIs, Bluetooth has become an Internet-compatible technology. IPv6 enables interoperability in the constructed IoT world, allowing networked devices to leverage technologies that best match their purpose and market positioning in existing IoT architectures. IPv6 allows Bluetooth devices to easily walk into the ecosystem of smart devices. Users can access Bluetooth Smart devices from the cloud through RESTful APIs and HTTP proxy protocols. IPv6 is an additional option for members of the Bluetooth Technology Alliance, allowing developers to create more solutions, not just for personal area networks. It is expanding into the wider Internet of Things.
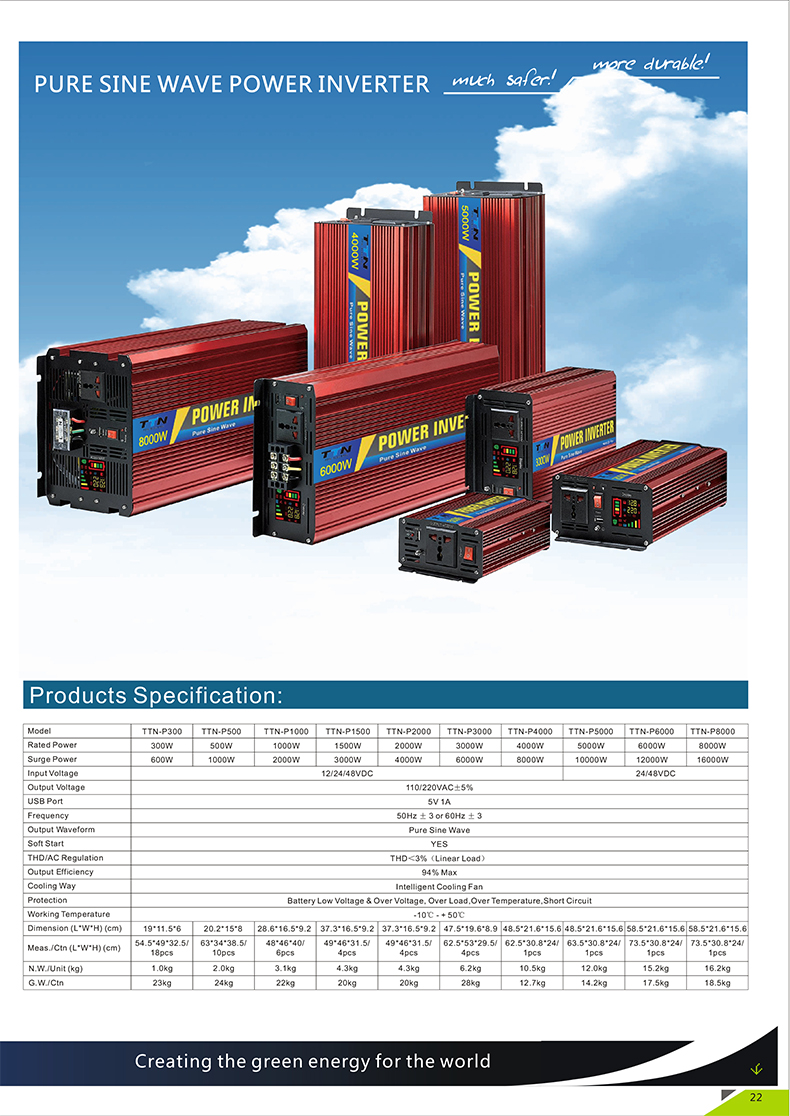
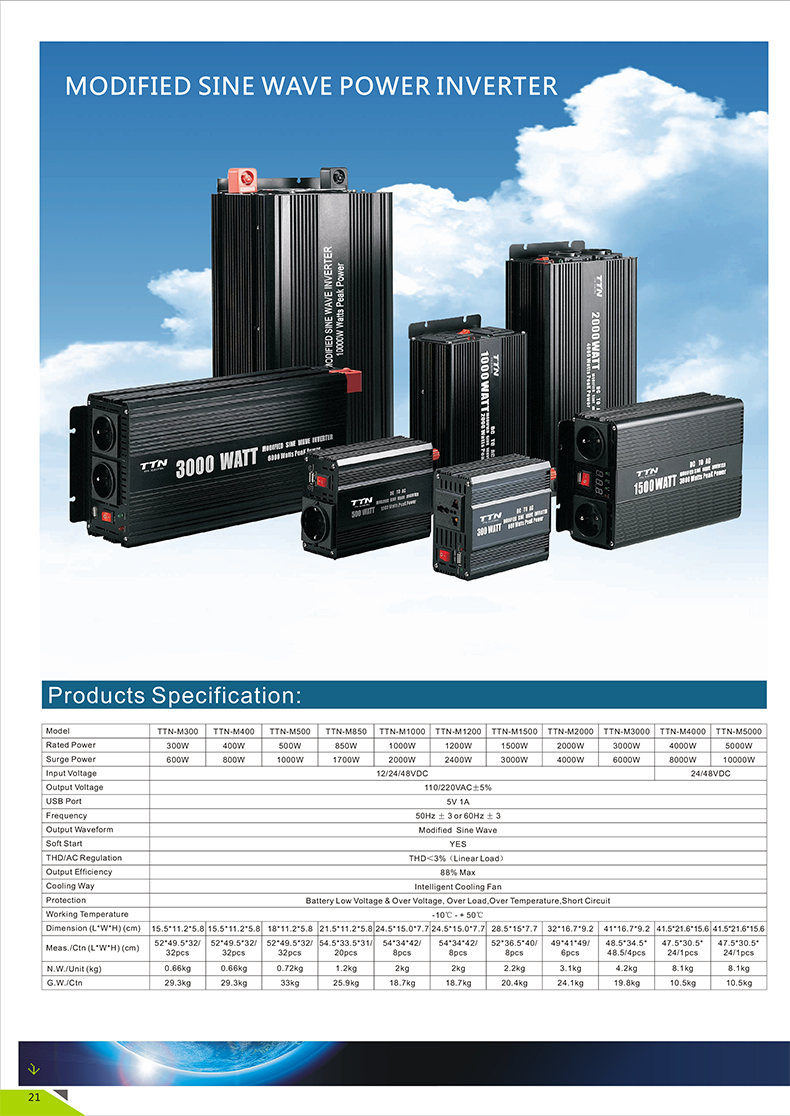
Products Description :
TTN Power inverter offer superior quality true sine wave output, it is designed to operate popular power tools and sensitive loads. Connect pure sine wave inverter with battery terninals, then you can get AC power for your appliances, the AC output identical to, and in some cases better than the power supplied by your utility.
Products Features :
- Input & output fully insolated.
- High Surge: high surge current capability starts difficult loads such as TVs,camps,motors and other inductive loads.
- Grounding Protection: there is terminal in front panel, you can grouding the inverter.
- Soft start: smooth start-up of the appliances.
- Pure sine wave output waveform: clean power for sensitive loads.
- AC output identical to, and in some cases better than the power supplied by your utility.
- Cooling fan works automatically when inverter becomes too hot, it turns off automatically when the temperature is reduced.
- Low total harmonic distortion: below 3%.
- Two LED indicators on the front panel showthe working and failure state.



Power Inverter,Modified Sine Inverter,Modified Square Wave Inverter,Modified Or Pure Sine Wave Inverter
zhejiang ttn electric co.,ltd , https://www.ttnpower.com