Automakers have begun to add advanced driver assistance systems to traditional passenger cars and gradually build roads to fully automated cars, but this is not the only way. Ok, so I have to ask a question: When will a fully-automobile car arrive? What will it look like?
Google has many years of experience in the field of autonomous driving. According to Google's prediction, fully automated vehicles will become a reality in 2020. At the 2016 AutomoTIve Forum, jointly organized by consulting firm JD Power, the National Association of Automobile Dealers (NADA) and the New York Auto Show, John Krafcik, CEO of Google's self-driving car project, delivered a speech introducing Google's self-driving car project. Progress.

Many people dream of having their own fully-automated driving car – you can comfortably lean on the seat or take a nap while driving, read news on your tablet, and even have a breakfast on the way to work. Although this kind of fully-automobile car still has a certain gap with reality, another self-driving car application may soon become a reality, and hopefully create a new market, that is, suitable for the disabled, visually impaired, and unable Self-driving cars for the elderly driving by themselves. This vision has excited NADA President Peter Welch, who also gave a speech at the forum.
Short-haul mileage travel
Krafcik said that the arrival of self-driving cars is "a process, not something that will happen at a certain point in time." As Welch envisioned, in the initial stage, these self-driving cars will first be used for users who have low demand for cruising range. Provide travel services. As technology continues to evolve, the cruising range of autonomous vehicles and the achievable maximum speed will increase, and the potential market segment will grow.
However, Krafcik said that Google's self-driving cars have a top speed of 25 mph (40 km/h), which can reduce the difficulty of development because the kinetic energy required at 35 mph (56 kph) is two at 25 mph. Times.
For many people who can no longer drive, the convenience of driving a car can be worth the cost of buying this car. Currently, Google has planned a precise driving route for its test vehicles. Therefore, such self-driving cars can also take a similar approach, providing the owner with a number of defined routes and, where possible, continuing to add new routes to meet new demands.
The self-driving car developed by Google uses an electric power system and is not equipped with a steering wheel and throttle, brake pedal. With a top speed of only 25 mph, the car is compliant with US regulators' definition of a smart "neighborhood car" that can travel in a relatively large adult community, many of which are located near shopping malls and medical facilities. Owners living in such communities may be satisfied with this slow but safe personal transportation, but basically the current vehicle is only suitable for use in good weather.
Google also owns a Lexus RX450h team, which has removed the steering wheel and throttle of these cars, brake pedals, and added an automatic steering system.
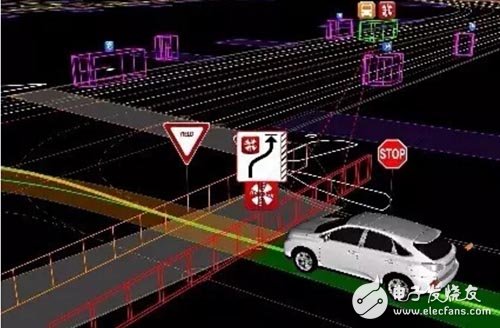
In this case, when Google "hears" the ambulance siren, it uses its own sensor to "observe" the surrounding area and make way at the intersection until the ambulance passes safely.
Predictive software
Google's autopilot software is specially written to have predictive capabilities, which means predicting the behavior of moving objects around the vehicle. According to Krafcik, software can usually predict whether a bicycle is going to overtake, or whether a pedestrian has to cross the street. At this point, the vehicle will slow down to a safe speed, stay away from the bike and make way for pedestrians. But Krafcik explained that the road environment can be very complicated. For example, on the streets of Hollywood, children will run around in costumes, something that has not been encountered elsewhere. At this point, Google cars can immediately determine that children's behavior is more difficult to predict than adults, especially when wearing school uniforms.
Google has long equipped Google cars with the ability to respond to emergency vehicles. Google Auto has a "snap" library with sirens for various emergency vehicles. For example, the fire truck is a long whistle, and the ambulance sounds shorter and sharper. Once the Google car "listens" to the siren, it will stop immediately and let the emergency vehicle pass through the intersection first. If the emergency vehicle needs to overtake from the rear, the Google car will slow down and stop.
According to Google, auto-cars will “apply to some people and part of the road environment first, and then gradually expand the scope of application to more people as technology continues to evolve.â€
Krafcik laughed and said that the Google car "is based entirely on data and measurement" and pointed out that the company's engineers have designed hundreds of tests and accumulated more than 1.5 million miles of real road test miles since 2009. . In addition, Google will perform a 3 million-mile simulation every day.
The road test for the Google project began as early as a section of the 101 National Road in California, where the car also carried the volunteers/drivers who volunteered to take the test.
Self-contained software
Krafcik said during the forum that regarding the Google project, it is worth mentioning that all current car software is self-sufficient. “Our autos work directly with the onboard processor and don't need the help of a cloud platform.†He said, “We don't rely on V2V (vehicle-vehicle) or V2X (vehicle-infrastructure) communication because of these two There are risks associated with downtime."
Drivers of fully automated vehicles can take over control of the car in special situations, such as sudden weather changes, high-speed blockades and high-speed speed limits, while Google's auto-driving car seems to be more complicated. However, due to the relatively limited range of use, Google cars seem to be easier to automate.
Currently, Google's two self-driving vehicles have been driving around the Google headquarters in Mountain View, California, and in the streets of Austin, Texas, and have accumulated experience in the rain in Kirkland, Washington. In addition, Krafcik said that Google has recently started snow testing, but he did not disclose more information.
The pie sensor at the top of Google's automated car has always been seen as the "wiper" of autonomous vehicles, but overall, the weather has a greater impact on the camera than on the lidar because the lidar can avoid the effects of raindrops on the line of sight. At this stage, if there is excessive rain, poor visibility and/or slippery road surface, Google will slow down and even stop to stop until the situation improves.
Prediction error
Self-driving cars do not completely avoid car accidents, especially in road environments shared with human drivers, even if this is the desire of autonomous car supporters. In February of this year, a car accident in Mountain View was widely reported: when waiting for a red light, a Google car is turning right to the right lane. At this point, the vehicle detected that the sandbag near the sewer blocked its own way. Therefore, the vehicle stops and lets a number of rear cars pass, and then slowly moves in the direction to prepare to exit. In the process, the vehicle "predicted" that a bus that was approaching would give way to itself, but the bus did not stop, and a minor accident happened.
Google’s autonomous car program is not alone, but is supported by a range of suppliers, including Bosch, ConTInental, FRIMO, LG Electronics, Prefix, RCO, and Roush Industries et al.
Krafcik said that legal issues must be resolved. It is reported that the state of California in the United States requires that a car driving on the state road must be equipped with a qualified driver. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), the agency believes that for the highest level of automatic vehicles (Class 4 or L4), robot control can be considered a “qualified driverâ€. In the event of an accident, the relevant economic responsibility is borne by the owner, but if the accident is caused by a vehicle defect, the manufacturer is responsible.
At present, some NGOs have raised objections to the interpretation of NHTSA, including the Consumer Watchdog in California. Automated vehicles require a fairly high level of “certificate of qualificationâ€. However, with the low-speed self-driving car, which is the constant optimization of the “park car†that everyone often hears, the potential market segment has been recognized and may be the first to form a scale.
SHENZHEN CHONDEKUAI TECHNOLOGY CO.LTD , https://www.szsiheyi.com