Recently, blockchain technology has attracted widespread attention. Although blockchain technology is currently developing rapidly, traditional blockchain technology has to be applied to commercial applications, especially financial applications. There are still many problems to be solved, such as transaction performance and privacy protection. One way to solve these problems is to re-develop new blockchains, but this approach will result in a lot of repetitive work and the need to continuously issue new digital assets. Then, whether there is a solution for upgrading the technology based on the original blockchain on the basis of not affecting the work of the original blockchain, the side chain is proposed in the context of such demand. This paper first introduces the basic concept of side chain, then analyzes the background and working principle of the side chain. Finally, the main side chain is introduced.

Basic concept
The sidechain protocol is essentially a cross-blockchain solution. With this solution, the transfer of digital assets from the first blockchain to the second blockchain can be achieved, and the second blockchain can be safely returned to the first block at a later point in time. chain. The first blockchain is often referred to as the main blockchain or the main chain, and each of the two blockchains is referred to as the sidechain. Initially, the main chain usually refers to the bitcoin blockchain, and now the main chain can be any blockchain. The sidechain protocol is envisioned as a way to allow digital assets to be transferred between the main chain and the sidechain, a technique that opens the door to new applications and experiments in the development of blockchain technology.
The technical details are hard to understand. My understanding is that current exchanges, online wallets, etc. are actually so-called sidechain applications, but they are centralized, closed, independent networks. Imagine that you transfer the bitcoin in your local wallet to the exchange address, then the closed network of the exchange gets the coins, so the transaction is credited to the exchange on the platform 1:1 equivalent to the exchange. Add these numbers to your account. Then you can use the "bitcoin" issued by the exchange on the trading platform to trade with people in real time, mortgage lending, and so on. Exchanges are an important application of the Bitcoin ecosystem, but they have problems like this (running, hacking, deficits, etc.), which are centralized, closed, independent networks. After you recharge your currency to the transaction, you can't actually control the coins, even though they are nominally yours. The current sidechain concept is essentially a separate, open, distributed network similar to Bitcoin, as opposed to a centralized, closed network such as an exchange.
Background
In 2012, for the first time in the Bitcoin chat room, a discussion about the concept of sidechains appeared. At the time, Bitcoin's core development team was considering how to safely upgrade the Bitcoin protocol to add new features, but adding functionality directly to the Bitcoin blockchain is dangerous because if new features fail in practice, It can have a serious impact on the existing bitcoin network. In addition, due to the network structure characteristics of Bitcoin, if you make large-scale changes, you need to get support from most Bitcoin miners.
At this time, the bitcoin core developers proposed a side chain solution.
This technique allows developers to attach new functionality to other blockchains, but these blockchains still attach to existing bitcoin blockchains. New features in these blockchains can take advantage of the existing Bitcoin network features without jeopardizing existing bitcoin networks.
In 2014, a number of blockchains with new functions appeared, and various competitive currencies such as Litecoin and Dogecoin were produced. At this time, the core development team of Bitcoin is worried that the production of these coins will dilute the value of Bitcoin. They believe that bitcoin should be used as a reserve currency and new features should be added to the sidechain. This way, if the user wants to use other new blockchain functions, there is no need to purchase other tokens.
“The biggest advantage of the sidechain is that it gives users access to a large number of new services. For example, you can move Bitcoin to another blockchain to take advantage of the privacy features of the corresponding blockchain, faster transaction speeds and smart contracts. ."
In order to transform the side chain from concept to reality, Bitstream, Matt Corallo and other bitcoin core developers jointly launched Blockstream, and in October of the same year, released the white paper "Enabling Blockchain InnovaTIons with Pegged Sidechains", which was clearly stated for the first time. The concept of sidechains and their protocol implementation.
Through the side chain, new functions such as transaction privacy protection technology and smart contracts can be added on the basis of the main chain, which allows users to access a large number of new services and has no impact on the work of the existing main chain. In addition, the sidechain also provides a safer way to upgrade the protocol, and when the sidechain has a catastrophic problem, the main chain remains intact.
The sidechain mechanism, in a nutshell, is a mechanism for moving money between two blockchains.
Xiao Ming: I have a bitcoin address and a Litecoin address. Can I send Bitcoin to the Litecoin address? Xiao Liang: No kidding, Bitcoin, Litecoin are two separate blockchains. How is this possible? Teacher: Xiaoliang said that Bitcoin and Litecoin are two separate blockchains. Now Bitcoin cannot be sent to the Litecoin address. Xiaoming’s idea is very creative. If the Litecoin blockchain becomes bitcoin After a side chain, Bitcoin can be sent to the Litecoin address. Similarly, if Bitcoin becomes the side chain of Litecoin, Litecoin can also be sent to the Bitcoin address. (Author: Huang Hongqing)
Implementation plan
The technical basis of the side chain implementation is two-way Peg. Through the two-way anchoring technology, it is possible to temporarily lock the digital assets in the main chain and release the equivalent digital assets in the side chain. When the equivalent digital asset is locked in the side chain, the digital asset of the main chain can also be released. The biggest difficulty in implementing bidirectional anchoring is that the protocol transformation needs to be compatible with the existing main chain, that is, it cannot affect the work of the existing main chain. The specific implementation methods can be divided into the following categories:
(1) Single hosting model
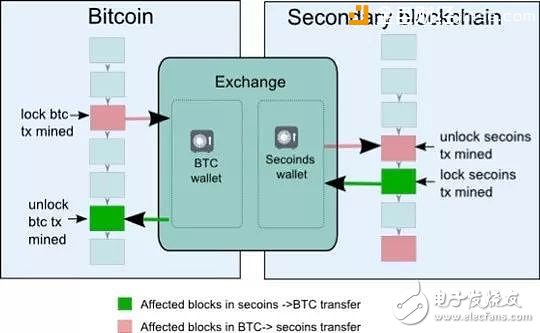
The easiest way to achieve bi-directional anchoring of the main chain and the side chain is by sending the digital asset to a single host of the main chain (similar to the exchange), and when the single host receives the relevant information, it is activated on the side chain. The corresponding digital assets. The biggest problem with this solution is that it is too central. Figure 1 shows the working principle of a single hosted mode with Bitcoin as the main chain:
(2) Alliance mode
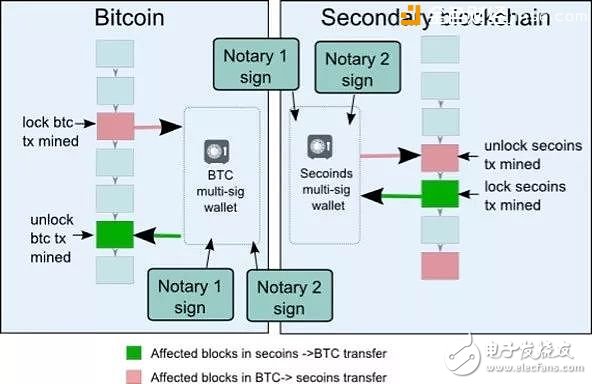
The alliance model uses a notary public union to replace a single custodian, using the multiple signatures of the notary public to confirm the flow of digital assets in the side chain. In this model, if you want to steal the digital assets frozen in the main chain, you need to break through more institutions, but the security of the side chain still depends on the honesty of the notary public. Figure 2 shows the working diagram of the alliance mode with Bitcoin as the main chain:
The biggest advantage of the single hosting mode and the federated mode is that they do not require any changes to the existing bitcoin protocol.
(3) SPV mode
The SPV (Simplified Payment VerificaTIon) model was originally conceived in the original sidechain white paper "Enabling Blockchain InnovaTIons with Pegged Sidechains". SPV is a way to prove the existence of a transaction, with a small amount of data to verify the existence of a transaction in a particular block.
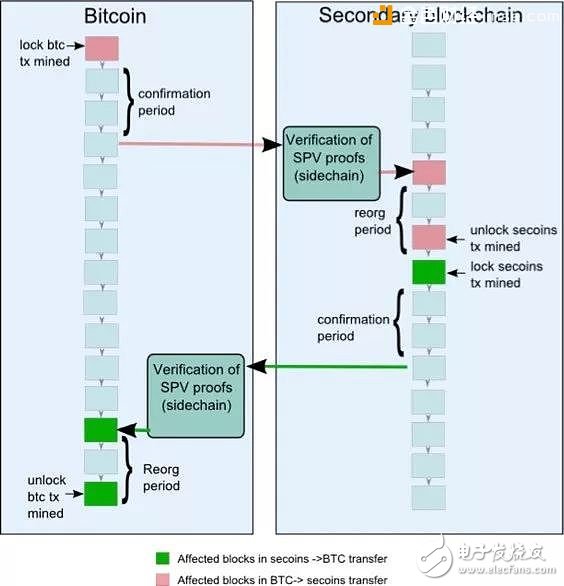
In SPV mode, the user sends the digital asset to a special address in the main chain on the main chain. This will lock the digital asset of the main chain, and the output will still be locked in the possible competition period to confirm the corresponding The transaction has been completed and an SPV certificate is created and sent to the side chain. At this point, a corresponding transaction with SPV certification will appear on the sidechain, while verifying that the digital assets on the main chain have been locked, and then opening another digital asset of the same value on the sidechain.
The use and change of such digital assets will be sent back to the main chain later. When this digital asset is returned to the main chain, the process repeats. They are sent to the locked output on the side chain. After a certain waiting time, an SPV certificate can be created to send it back to the main blockchain to unlock the digital assets on the main chain. The problem with the SPV mode is that it requires a soft fork of the main chain. Figure 3 shows the workflow of the SPV mode in the bitcoin backbone:
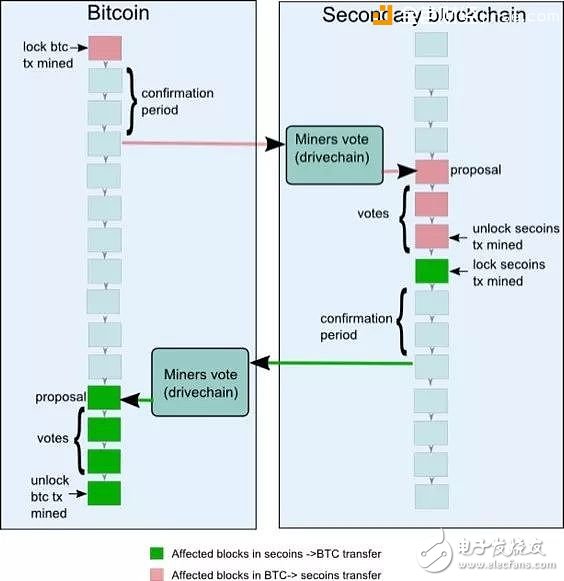
(four) drive chain mode
The concept of the drive chain was proposed by the founder of Bitcoin Hivemind, Paul Sztorc. In the drive chain, the mine works as an 'algorithm agent guardian', detecting the current state of the side chain. In other words, the miners are essentially fund custodians, and the drive chain will be supervised by locked digital assets to the hands of digital asset miners, and allow miners to vote when to unlock digital assets and where to unlock unlocked digital assets. . The miners observe the status of the side chains and when they receive the request from the side chain, they implement a coordination agreement to ensure that they agree on the authenticity of the requirements. The higher the participation of honest miners in the drive chain, the greater the overall system security. Like the SPV side chain, the drive chain also requires a soft fork of the main chain. Figure 4 shows the workflow of the drive chain mode with Bitcoin as the main chain:
(5) Mixed mode
All of the above modes are symmetrical, and the mixed mode is a mode in which the above-described method of obtaining bidirectional anchoring is effectively combined. Because the main chain and the side chain are different in the implementation mechanism, the symmetric two-way anchoring model may not be perfect. The hybrid mode uses different unlocking methods for the main chain and the side chain, such as using the SPV mode on the side chain and the drive chain mode on the main chain network. Similarly, the blend mode also requires a soft fork of the main chain.
Typical example
At present, the well-known side chains include bitcoin network-based side chain BTC Relay, Rootstock's Liquid, and non-bitcoin side chains such as Lisk and domestic Asch.
BTC Relay is a sidechain solution based on the Ethereum blockchain-based smart contract launched by ConsenSys. BTC Relay connects the Ethereum network to the Bitcoin network in a secure decentralized manner. BTC Relay allows users to verify bitcoin transactions on the Ethereum blockchain by using Ethereum's smart contract feature. Ethereum DApp developers can make API calls from smart contracts to BTC Relay to verify Bitcoin network activity.
Liquid is Blockstream's open source sidechain project, which uses bitcoin two-way anchoring technology. Liquid aims to enable Bitcoin to be interchanged in the main chain and sidechain, with the aim of increasing privacy, reducing costs, accelerating exchanges and brokerage. Value transfer and settlement process between businesses.
Lisk is a blockchain platform dedicated to creating distributed applications for JavaScript developers. It was founded in early 2016 by Max Kordek and Oliver Beddows in Germany. It runs every distributed application on its own and unique blockchain, the sidechain, which makes the main Lisk main network efficient, fast and streamlined. Asch is a domestically based sidechain. The decentralized application platform for technology was established in October 2016 by Shan Qingfeng. The services provided by the Asch platform include a main chain and a suite of application development kits. Asch's main chain is mainly responsible for building infrastructure, data sharing between applications and asset routing. The application development toolkit has a built-in sidechain protocol, which is mainly responsible for building specific applications. Assets can be interconnected with the main chain through sidechain protocols.
to sum up
Sidechains are the goal of a cryptocurrency financial ecosystem in a convergent manner, rather than rejecting existing systems like other digital assets. Sidechain technology further expands the application range and innovation space of blockchain technology, enabling traditional blockchains to support multiple asset types, as well as small and micropayments, smart contracts, secure processing mechanisms, property registration, etc., and can enhance blocks. Chain privacy protection. With sidechains, we can easily create a variety of intelligent applications such as financial contracts, stocks, futures, derivatives and more.
Supplementary reading
Some notes
1. Bitcoin is still bitcoin when it is circulating in the side chain. The bitcoin of the side chain and the bitcoin of the main chain are usually 1 to 1 exchange rate, and may have a predetermined exchange rate. 2, the side chain mining can not produce bitcoin, the side chain may have its own currency, or may not have its own currency, only for the circulation of bitcoin. 3. The side chains may be equivalent and non-equivalent. The peer side chains exist independently, which can also be the backbone. The main sides are mutual, and if there is enough demand, Bitcoin can also become the side chain of Litecoin. Non-equivalent side chains are dependent on the backbone. 4, decentralization has not changed, everyone or company can create their own bitcoin side chain, users and miners agree that will become mainstream. 5, of course, the side chain should have enough computing power to ensure the reliability and safety of the side chain. 6. The side chain white paper proposes a clear side chain frame, and how the specific side chain can be realized allows the designer to freely play.
Some creative ideas that the sidechain might achieve
1. The detention fee, that is, the long-term non-moving currency, will be devalued over time, and the amount subtracted will be returned to the miners. For example, coins that have not been moved for more than one year are depreciated by 10% each year. In today's bitcoin network, there are often big customers who lose their keys and the corresponding coins are lost. This will reduce the sufficiency and liquidity of the currency of the Bitcoin economy and is considered a potential risk for Bitcoin. Through the detention fee, the currency flow is encouraged, the miners are encouraged, and some coins lost due to lost keys can be recovered. 2, the new mining income agreed that the miner's computing power will threaten the network security, will deduct mining income. For example, a miner with a power of more than 50% does not have a reward, which can constrain the miner's control power and prevent 51% of attacks. 3. The extension payment agreement for mining income. Now, the miners get rewards and transaction fees immediately after they dig into the mine. This agreement delays the payment of mining proceeds. For example, after mining the 100 blocks of the mine, pay the mining income. This helps to encourage miners to maintain the proper functioning of the network. 4. The address can be used regularly. Added a time-related address. The currency of the address can only be used until a certain time has elapsed. For example, people can send 10 coins to this type of address and set it up after 10 years. When time is not up, no one, including the owner, can move the coins inside.
This is just part of the creative idea, you may also have your own ideas, and the creative ideas of the Bitcoin community are endless. Each idea has its own advantages and disadvantages, sidechains, providing us with a mechanism that does not interfere with testing and upgrades.
Uv Curing Hd Film,Curved Tempered Glass,Plastic Screen Protector,Mobile Film Cuttting Machine
Shenzhen TUOLI Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.hydrogelprotector.com