Understand the characteristics and applications of the next NB-IOT.
Foreword Last year, NB-IoT (Narrow Band Internet of Things, narrow-band cellular internet of things) as an important topic of 3GPP R13, its corresponding 3GPP protocol-related content was approved by the RAN plenary session, and formally announced this widely supported by the wireless industry. The NB-IoT standard core agreement was finally completed after more than two years of research.
Huawei also formally launched an end-to-end NB-IoT solution at this year's World Mobile IoT Summit, making the Internet of Things one of the carriers' future basic services. The solutions mainly include intelligent terminal solutions enabled by Huawei LiteOS and NB-IoT chips, eNodeB base stations that have been successfully evolved to NB-IoT, IoT Packet Core that can support flexible deployment of Core in a Box or NFV slices, and cloud-based architecture. The IoT connection management platform, which has big data capabilities, meets the core requirements of carrier low-power wide area coverage for IoT services.
Text - Background
According to relevant reports, as of the end of 2015, the total number of Internet of Things connected users of the three major operators in China has approached 100 million. According to the research and development center of the Internet of Things of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the total revenue of the domestic Internet of Things industry in 2016 will exceed one trillion yuan. Today, the proportion of IoT technologies used in the industry has increased year by year, infiltrating the manufacturing industries, transportation logistics, health care, consumer electronics, retail, and automotive applications industries. The era of interconnectedness is entering our lives in an extremely rapid pace.
There are many wireless communication technologies for the Internet of Things, which are mainly divided into two categories: one is the short-range communication technology such as Zigbee, WiFi, Bluetooth, and Z-wave, and the other is the low-power Wide-Area Network (LPWAN). ), namely wide area network communication technology. LPWA can be divided into two categories: one is LoRa, SigFox and other technologies that work on unlicensed spectrum; the other is on 2/3/4G cellular communications technologies working under licensed spectrum, such as EC-GSM, supported by 3GPP. LTE Cat-m, NB-IoT, etc.
According to the network transmission rate classification, as shown in the figure.
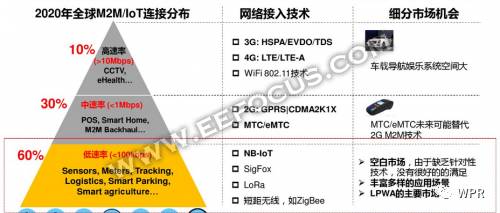
From the above figure, we can see that high-speed services mainly use 3G and 4G technologies; medium-rate services mainly use GPRS technologies. Low-rate services currently do not have very good cellular technology to satisfy, but it has a variety of application scenarios, and in many cases, it can only be supported using GPRS technology.
Therefore, based on the keen insight into the trend and demand for cellular networking, in early 2013, Huawei and industry consensus operators, equipment vendors, and chip vendors jointly conducted extensive and in-depth needs and technical discussions, and quickly reached an agreement. The consensus of the development of the narrowband cellular Internet of Things industry, NB-IoT research officially began. What is the history of the evolution of the NB-IoT standard? You continue to look down.
Evolution history of NB-IoT standard
In early 2013, Huawei launched narrowband cellular Internet of Things (IoT) development with related industry vendors and operators and named LTE for Machine to Machine (LTE-M). In the LTE-M technical solution selection, there are mainly two ideas at that time: one is based on the existing GSM evolution ideas; the other is a new airline idea proposed by Huawei, then the name is NB-M2M.
In May 2014, the “Cellular System Support for UltraLow ​​Complexity and Low Throughput Internet of Things†SI supported by Vodafone, China Mobile, Orange, Telecom Italy, Huawei, Nokia, etc. was established in the 3GPP GERAN Working Group, and the name of LTE-M was established. It evolved into Cellular IoT, referred to as CIoT.
In April 2015, an important decision was made at the PCG (Project Coordination Group) meeting: After CIoT completed GE in GERAN, the WI phase had to go to the RAN to establish and complete related agreements.
In May 2015, based on the consensus, Huawei and Qualcomm jointly announced a converged solution. That is, the uplink uses FDMA multiple access, and the downlink adopts OFDM multiple access. The name of the integrated solution is called NB-CIoT (Narrow Band Cellular IoT).
On August 10, 2015, at the last meeting of the GERAN SI stage, Ericsson and several companies proposed the concept of NB-LTE (Narrow Band LTE).
In September 2015, the RAN #69 meeting was heatedly discussed. The parties finally reached an agreement that the two NB-CIoT and NB-LTE technologies were merged to form the NB-IoT WID. NB-CIoT evolved to NB-IoT (Narrow Band IoT).
On June 16, 2016, the NB-IoT R core protocol was frozen in the four working groups RAN1, RAN2, RAN3, and RAN4. The performance specification is in the 3GPP RAN4 working group and is scheduled to end in September. The performance specifications NB-IoT and eMTC are conducted simultaneously and the plan is completed at the same time.

Practical Application of NB-IoT Solution
Here are some NB-IoT related applications that will give you a deeper understanding of what it means.
(1) Huawei/China Unicom's NB-IoT Intelligent Parking Solution: This smart parking system based on Huawei's NB-IoT module will be able to achieve reservations, sub-lease parking spaces, low power consumption and high penetration capabilities. This solution is more reliable. At present, the parking system has been commercialized in Shanghai Disneyland.

(2) ZTE/China Mobile's smart manhole cover: This program can supervise the condition of manhole covers in all directions and can provide timely warning when the manhole cover is opened and shifted. NB-IoT technology has features such as low cost, wide coverage, low power, and large connections, which can effectively improve the coverage area of ​​the intelligent manhole cover monitoring system, eliminate coverage dead angles, and reduce construction and maintenance costs.
(3) China Mobile/Ericsson/Intel's environmental detection applications: Intel's latest NB-IoT chip (XMM7115) can be used to monitor the environment's PM value, temperature, humidity, brightness, and other brightness in real time.

NB-IoT Development and Challenges
First talk about the advantages and value of the NB-IoT solution: 1. Wide and deep coverage: 20 dB+ enhancement over GPRS coverage; 2. Low power consumption: AA battery based lifespan of more than 10 years; 3, Low cost; Large connection: 50k+ user capacity/200kHz cell.
With these advantages, NB-IoT technology has attracted the attention of mainstream operators and equipment manufacturers around the world. With the freezing of standards, NB-IoT will usher in commercial use in September this year. According to relevant reports, China Unicom plans to promote the commercial deployment of NB-IoT in key cities early this year and early next year. In addition, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) also held a narrow-band IoT work promotion meeting in April to build a scale outfield experiment based on the NB-IoT standard at the end of the year. According to relevant market surveys, 50 mainstream operators worldwide will support NB-IoT by the end of this year, and NB-IoT will cover 1/4 of the IoT connections in the future. By 2020, M2M devices will reach 7 billion connections.
NB-IoT is a brand-new standard technology and is under competitive pressure from Sigfox and LoRa technologies (the industry chain is relatively mature and commercialization is used earlier). However, Sigfox and LoRa are unlicensed bands and are not expected by operators and equipment vendors. Although the NB-IoT market has broad prospects, there is also a price war behind it. The cost of NB-IoT is very low, the cost will be reduced to 1 US dollar for large-scale applications, and the current single connection module still stays at 5 US dollars. The price of Bluetooth, Thread, and ZigBee chips is around US$2. Only one of the standard chip prices is less than US$1. This price gap allows companies to consider the cost advantage when thinking about NB-IoT. Although operators are actively promoting, there is still a long way to go before truly realizing the productization of technology.
Air conditioning heating: After turning on the heating function, the high-temperature coolant in the engine will flow through the heating water tank. At this time, the air blown by the blower will also pass through the heating water tank, so that the air outlet of the air conditioner can blow warm air. Refrigeration of car air conditioner: After pressing the ac button, the compressor clutch of the car air conditioner will be engaged. At this time, the engine will drive the compressor to operate. The compressor can continuously compress the refrigerant and deliver the refrigerant to the evaporating box. The refrigerant is evaporating The inside of the box will expand and absorb heat so that the refrigerant can cool the evaporating box.
Blower Fan,Centrifugal Blowers,Industrial Blower,Air Blower Fan
Original Electronics Technology (Suzhou) Co., Ltd. , https://www.original-te.com